Extensor Digitorum Brevis Brevis Flap
Anatomic considerations
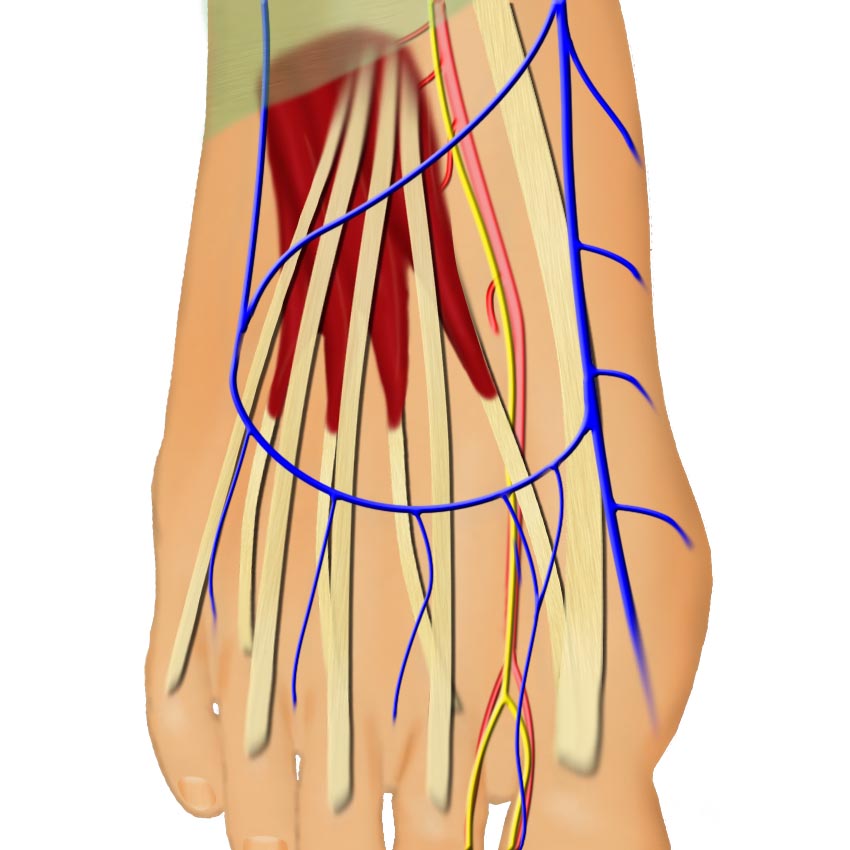
Anatomy
The extensor brevis muscle has proximal muscle bulk and 4 tendinous insertions into the long toe extensors. The body of this muscle originates on the talo-calcaneal ligament and the inferior calcaneus on the lateral foot. The extensor hallucis brevis (the most medial slip) inserts on the proximal phalanx of the great toe. The extensor digitorum brevis (the lateral three slips) inserts on the second, third, and fourth toe extensor tendons. This muscle lies just deep to the longus extensor tendons.
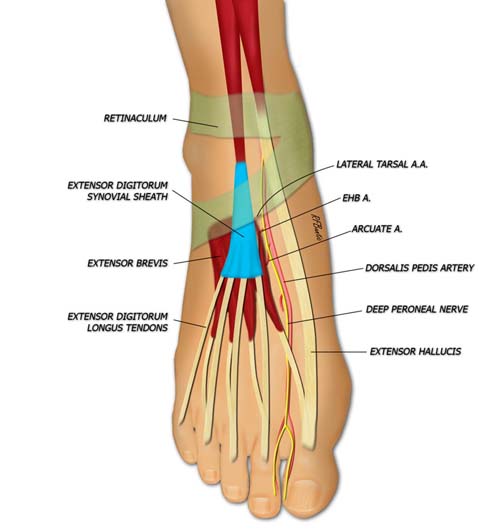
Two lateral branches from the dorsalis pedis artery supply the extensor brevis muscle: the lateral tarsal artery and the artery to extensor hallucis brevis, respectively. The muscle is innervated by a branch of the deep peroneal nerve.